Necessary Always Active
Necessary cookies are required to enable the basic features of this site, such as providing secure log-in or adjusting your consent preferences. These cookies do not store any personally identifiable data.
|
||||||
|
||||||
|
||||||
|

Think of a world where the software is not only a collection of pre-programmed software, but also a smart system that learns, adapts and decides on its own. AI agents are bringing it to life! These AI agents are subsidiary assistants to virtual assistants that maximize sales from intelligent programs. By simplifying worldly works, maximizing efficiency and increasing decision making, they are bringing revolution in the way companies operate.
AI and Robotics are changing the way of doing business, automating monotonous tasks and making better decisions in various industries. AI agents are different from traditional software as they are capable of working independently, learning from data and changing according to new situations without any human intervention. In this blog, we will discuss how AI agents work, their advantages and disadvantages with their development.

AI agents have developed greatly with basic rules-based systems, ranging from sophisticated autonomous systems to learning and adaptation. The initial AI agents acted on a certain command basis, reacted to pre-defined input with minimal flexibility. With the development of artificial intelligence and machine learning, modern AI agents now process large amounts of data, recognize patterns, and make real -time decisions.
Today’s AI agents integrate natural language processing, reinforcement learning and nerve network, allowing them to interact with humans, predict the outcomes and optimize operations in industries. As AI technology advances, these agents are becoming more autonomous, intelligent and necessary to run innovation in various fields.
AI agents operate by examining their surroundings and data to meet specific objectives. Unlike traditional software, which follows set instructions, agents for businesses utilize advanced technologies like machine learning, deep learning, and natural language processing to understand data and work towards their goals. These AI agents evolve by learning from their interactions that help them in becoming a decision-making support system for the users.
Adaptability makes AI agents essential across various sectors, from customer service robots to tackling intricate challenges in finance, healthcare, and cybersecurity.
Key components of how AI agents work:
By integrating these capabilities, AI agents enhance efficiency, automate tasks, and drive intelligent decision-making across industries.
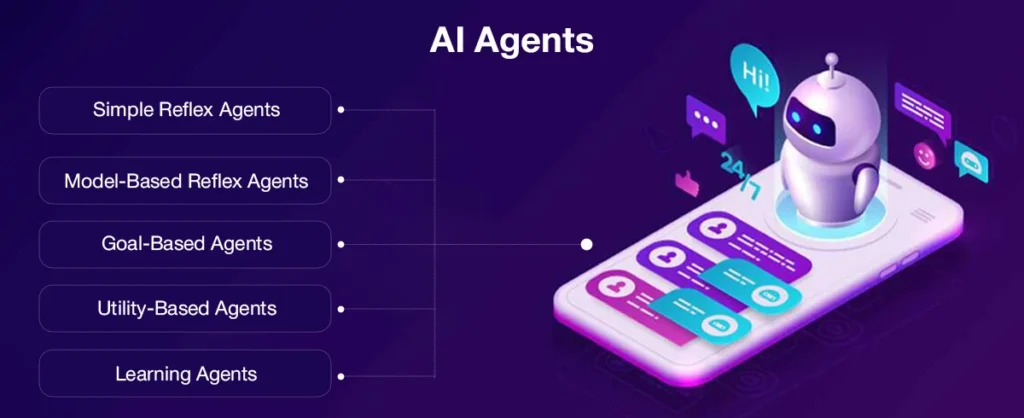
AI agents are classified according to their complexity, learning ability and autonomy. They can be simple as rules-based systems or can be complicated as advanced agents that learn and develop over time. The following are the primary types of AI agents, examples of the real world reflect their use.
Simple reflex agents work by certain rules and only respond to the current situation without learning or remembering previous experiences. They perform well in predictive situations but are challenged with complex or dynamic conditions.
Conversational AI agents use model-based reflex systems to realize context, remember previous interactions, and make decision-making choices. In contrast to basic reflex agents, they are able to cope with changing environments by examining prior conversations, guaranteeing more customized and context-oriented responses.
The goal-based agents take AI a step forward by defining and analyzing various tasks to meet them. They apply planning strategies and search algorithms to decide the most appropriate action.
Utility-based agents are beyond the target determination by evaluating various results and providing a value to each. These intelligent agents in AI consider factors such as risks, costs and user preferences to determine the most efficient action.
Learning agents continuously improve their decisions by applying machine learning. They learn from experience, change strategies through experiment, and increase performance on previous experiences.
AI agents are bringing a revolution in industries by automating and streamlining processes and making better decisions. Their ability to work independently, learning from experience and user interactions, makes them an asset for individuals and businesses. Some of the major benefits of are as follows:
While AI agents provide many benefits, they also face challenges that affect their effectiveness, deployment and long -term success. These challenges arise from technical, moral and operating limitations, which businesses must address to maximize AI’s ability.
AI agents rely on vast amounts of high-quality data to act accurately. Incomplete, biased, or older data can cause incorrect decisions and incredible results.
AI agents can inherit the prejudices present in their training data which can lead to inappropriate or biased decisions. Addressing prejudice and ensuring moral AI use is a major challenge for businesses and developers.
AI agents often process sensitive users and commercial data, making them an easy target for cyber hazards. Ensuring data privacy and securing the AI model against adverse attacks is important for safe deployment.
Many AI models, especially deep learning-based agents, function as “black boxes”, making it difficult to understand how they derive a particular conclusion. This lack of transparency can reduce confidence and obstruct regulatory compliance.
Despite their autonomy, AI agents still require human monitoring and intervention to handle unexpected scenarios, errors, or ethical dilemmas. Finding the right balance between automation and human oversight remains a challenge.
AI agents are changing industries, but their increasing effect comes with risks. While business takes advantage of AI for automation and decision making, challenges such as data security and moral concerns should be addressed. The Dark Web has already seen AI-powered cyber threats, from deepfake scams to automatic hacking, proving that these technologies can be exploited.
The attention should not be on how to make the AI stronger but how to ensure that it’s deployed responsibly. Security, fairness, and transparency must guide the development of AI so that it’s not used incorrectly. Those organizations that find the right balance between risk avoidance and innovation will define the future of AI in a responsible way. The true question isn’t if AI agents will reshape industries, but whether we are ready to steer this change in the right direction—maximizing benefits while mitigating threats.
Sign up to receive our newsletter featuring the latest tech trends, in-depth articles, and exclusive insights. Stay ahead of the curve!