Necessary Always Active
Necessary cookies are required to enable the basic features of this site, such as providing secure log-in or adjusting your consent preferences. These cookies do not store any personally identifiable data.
|
||||||
|
||||||
|
||||||
|

Imagine stepping into a digital world that feels as real as your physical environment. XR is driving a new wave of digital transformation by creating possibilities to seamlessly blend the physical and digital worlds.
A recent research about advancing technology for humanity and earth by Steve Mann and colleagues suggests that XR is the “physical spatial metaverse”. This means that Extended reality is integrating the physical world, the virtual world of artificial intelligence and the social world of human interaction.
In 2023, the global XR market cap was valued at approximately $131.54 billion and that number is expected to skyrocket by 10 times up to $1.7 trillion by 2032. The potential of XR to revolutionize various industries is simply mind-blowing.
Extended Reality has recently become more common due to its ability to change the way we learn and work. Today, medical students can practice surgery with Virtual Reality, shoppers can try on new clothes with Augmented Reality, and you can have MR meetings where digital 3D objects can be discussed in real time.
The line between our digital and physical world is blurring and XR is at the forefront. In this article, we will discuss the significance of XR in digital interaction, explain the key components in XR and also provide examples to help you understand how XR is replacing old practices in different industries with immersive experiences.
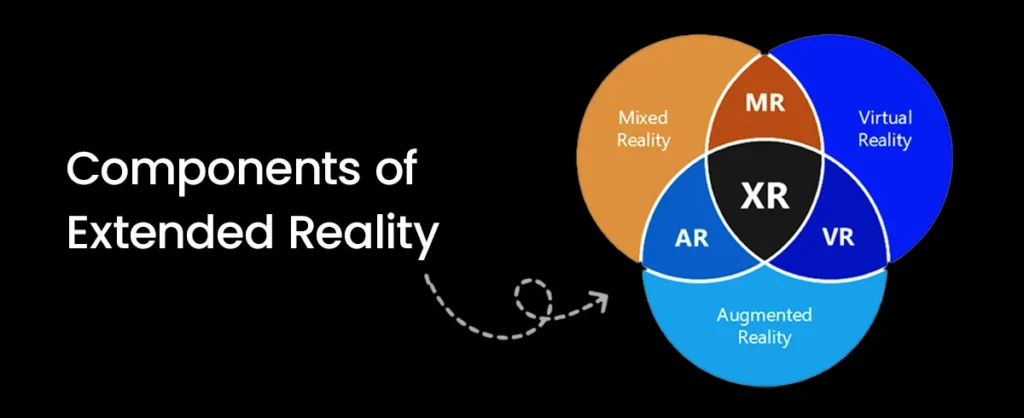
Did you know the “X” in XR doesn’t actually mean “Extended”?
It’s a variable that can stand for Virtual Reality, Augmented Reality, or Mixed Reality. This is why XR, which stands for Extended Reality, is used as a general term for all immersive technologies.
So what is XR all about?
XR refers to any technology that enhances or changes our real-world experience by introducing digital elements. This includes fully immersive virtual experiences, digital overlays on our surroundings, or a combination of both.
How does XR support learning and training?
XR places learners in lifelike environments that improve memory and understanding in ways traditional methods often can’t. It makes learning more interactive and fun through gamification. In areas like healthcare, XR provides realistic training simulations that allow learners to practice complex procedures safely.
Here’s how each type of XR works:
Virtual Reality completely takes you into a digital environment
Augmented Reality adds digital content to what you see in the real world
Mixed Reality blends the digital and physical worlds so they interact with each other
To power these experiences, XR uses several advanced technologies like
To help you understand XR better, we will provide an overview of what you need to know about the latest immersive technologies: VR, AR and MR.

One of the key technologies within XR is Virtual Reality (VR). It uses a headset or head-mounted display to create a fully immersive and simulated environment for users to interact with. It functions as a seamless transition from the physical world to a virtual one. One moment, the user is in a physical room and the next, they are immersed in a 360-degree virtual environment.
The latest VR devices push these boundaries offering an environment that looks and behaves like the real world. Most times it triggers the users to believe they are stepping into an artificial world created by VR developers. For example, a VR experience can make users feel as though they are walking on the moon or standing atop a skyscraper, preparing to board a helicopter.
The early industry adopters of VR were the gaming and entertainment industry. Today, companies in several industries such as healthcare, construction, engineering, and the military have incorporated the use of Virtual reality. VR offers virtual training simulations used by pilots, surgeons and military personnel to safely learn and practice complex procedures.
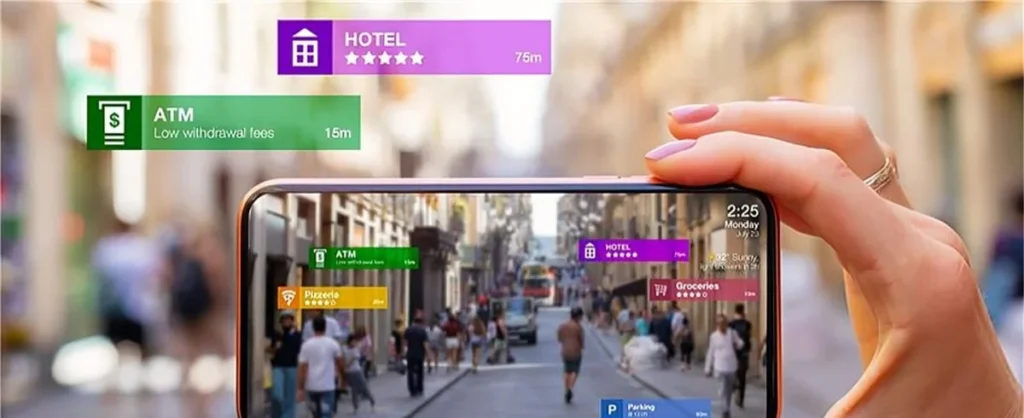
Another component of XR is Augmented reality (AR). While Virtual Reality (VR) immerses users in a completely digital environment, Augmented Reality (AR) enhances the real world by overlaying virtual elements such as images, text, animation, drawings, allowing users to interact with digital content while remaining aware of their actual surroundings.
One of the most notable integrations of Augmented Reality (AR) into everyday life is the mobile game Pokémon GO, which overlays virtual Pokémon onto real-world locations, encouraging players to explore their surroundings.
Similarly, Netflix has utilized AR for immersive promotional experiences; for instance, to promote Stranger Things, they launched AR-enabled print ads in The New York Times that, when scanned with Google Lens, revealed interactive content related to the series. However, while Netflix has explored AR in marketing campaigns, it has not yet fully adopted Extended Reality (XR) technologies as a core component of its video content delivery.
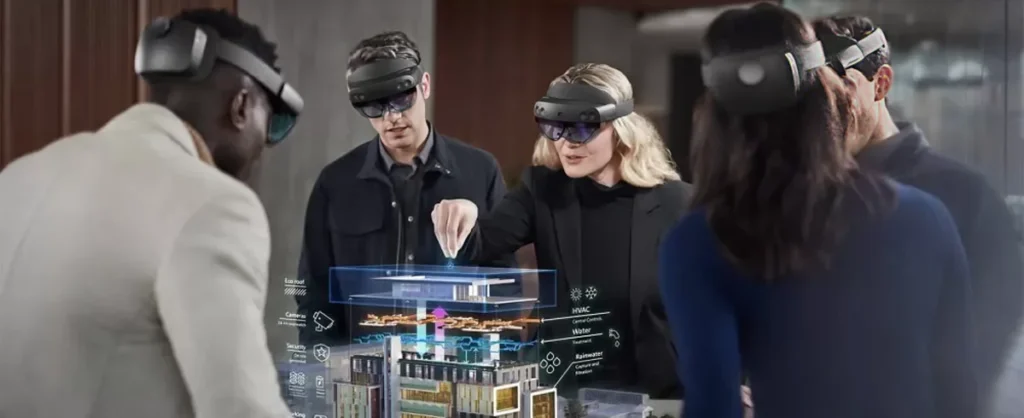

Mixed Reality allows users to directly interact with the digital and physical worlds at the same time providing a seamless integration of the real world and rendered graphics. MR offers a mixed interaction blending the real and virtual objects that are presented in a single display.
Mixed Reality (MR) encompasses two primary approaches: integrating virtual objects into the real world and bringing real-world elements into virtual environments. For instance, devices like the Microsoft HoloLens allow users to see and interact with holographic images superimposed onto their actual surroundings, blending digital content seamlessly with the physical world.
Conversely, technologies such as Apple’s Vision Pro utilize external cameras to capture the user’s real environment and display it within a virtual space, enabling interactions with both real and virtual elements simultaneously.
Finally, users can experience MR environments through a headset, phone or camera and can interact with digital objects by moving them around or placing them in the physical world.
XR’s ability to enhance reality opens numerous opportunities across various sectors:
Gaming and entertainment have experienced the most obvious transformations through XR. VR games immerse players into incredibly realistic digital environments, enhancing interaction and engagement. Multiplayer XR games further enrich experiences, allowing people from around the world to share immersive adventures.
XR is revolutionizing healthcare by providing realistic virtual training for medical professionals. Surgeons now practice complicated procedures through VR simulations, significantly reducing risks during actual surgeries. Telemedicine is also enhanced through XR, enabling remote patient monitoring and more interactive virtual consultations.
The educational sector greatly benefits from XR’s interactive and immersive capabilities. Students engage better when abstract concepts become visually and experientially accessible. XR technology is widely used in vocational training, from mechanics repairing virtual engines to electricians learning wiring through realistic simulations.
XR significantly enhances customer experiences in retail by providing interactive and immersive shopping experiences. Shoppers virtually try clothes, accessories, or makeup, enhancing confidence in their purchases. Retailers utilize AR for immersive product demonstrations, greatly increasing customer engagement and satisfaction.
Brands are increasingly using XR to create engaging and interactive experiences that drive customer loyalty. AR filters on social media platforms like Instagram and Snapchat allow businesses to connect with users in playful and memorable ways. Interactive product demos and XR-enhanced storytelling also help brands stand out in competitive markets.
Mixed Reality is improving how teams collaborate, especially in industries like architecture, engineering, and design. Teams can work on shared 3D models in real time, regardless of location, reducing the need for physical meetings while improving the quality and speed of decision-making.
Rapid advancements in hardware, AI, and connectivity technologies are accelerating XR’s growth:
Advancements in hardware have made XR more comfortable, accessible, and effective. Cutting-edge headsets like Meta Quest, Apple Vision Pro, and HTC Vive deliver high-quality visuals, superior comfort, and immersive audio experiences. Innovations such as haptic gloves and XR glasses enhance user interaction and realism.
Artificial Intelligence significantly improves XR by creating highly realistic environments, adaptive learning scenarios, and personalized user experiences. AI-powered XR applications generate lifelike avatars, enhance realism through intelligent scene rendering, and continuously adapt interactions based on user behaviors. In virtual environments, AI enables features such as smart NPCs (non-player characters) and dynamically generated settings, making the experience more lifelike and interactive.
One innovative use case of 5G technology is augmented reality in sports, which enables seamless streaming of live events with interactive, real-time overlays. 5G significantly boosts XR by providing high-speed connectivity and minimal latency, essential for seamless, immersive experiences. With 5G, XR applications can stream high-quality content directly to devices without lag, enhancing real-time interaction and accessibility.
Cloud-based XR further enables widespread and affordable access to XR technology by reducing hardware dependency. Services like NVIDIA CloudXR allow businesses to stream immersive content from powerful servers to mobile and wearable devices, enabling complex XR applications without the need for high-end hardware.
Despite its incredible potential, XR faces several critical challenges:
High initial costs remain a barrier for widespread XR adoption. High-end XR hardwares such as headsets can be costly, limiting broader accessibility. Companies are working to democratize XR technology by creating affordable solutions and subscription-based models to reduce upfront costs.
XR technologies collect significant user data, raising privacy concerns. Ensuring data security and transparent user consent remains vital. Users must clearly understand how their data is used, stored, and protected to avoid misuse or cybersecurity breaches.
Extended XR usage poses potential health risks like eye strain, motion sickness, and other physical discomforts. Psychological impacts are also concerning, with issues like addiction or difficulty distinguishing between reality and virtual experiences. Responsible usage guidelines and awareness campaigns are essential to mitigate these risks.
Looking ahead, XR is poised to further integrate into daily life, with advancements in areas like mental health therapy, where virtual environments assist in treating conditions such as anxiety and PTSD. As technology continues to evolve, XR will offer more immersive, interactive, and personalized experiences, transforming how we work, learn, and connect.
Extended Reality (XR) isn’t just another digital trend; it’s a transformative technology reshaping industries and our daily lives. From gaming and entertainment to healthcare, education, retail, and beyond, XR unlocks unprecedented opportunities for innovation, engagement, and interaction. As technological advancements address current challenges, XR will become increasingly accessible, realistic, and integral to everyday life, making our digital interactions more immersive and meaningful than ever before.
Sign up to receive our newsletter featuring the latest tech trends, in-depth articles, and exclusive insights. Stay ahead of the curve!