Necessary Always Active
Necessary cookies are required to enable the basic features of this site, such as providing secure log-in or adjusting your consent preferences. These cookies do not store any personally identifiable data.
|
||||||
|
||||||
|
||||||
|

In Focus
The evolution of mobile networks has consistently redefined the way humans communicate, share data, and experience the digital world. From the first generation of mobile technology, which introduced voice calls, to the fifth generation (5G) that brought unprecedented data speeds and ultra-low latency, each phase has pushed the boundaries of innovation. In this article, we will be discussing the difference between 6G vs 5G in detail.
5G is still in the process of global deployment, but research and development for 6G have already begun across leading technology hubs. Companies and research institutions are investigating how 6G could transform communication systems and enable new digital experiences, potentially marking the next-gen technologies in mobile connectivity. This forms the core of the 6G vs 5G comparison.
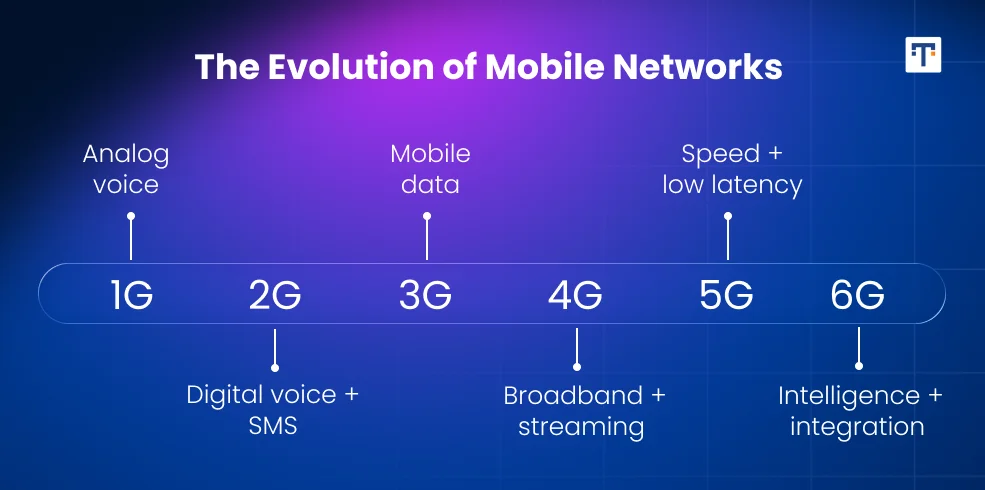
Fifth-generation technology, or 5G, represents a major leap from its predecessor, 4G LTE is important to understand. It was designed to deliver higher data rates, reduced latency, and greater reliability. 5G technology can theoretically reach speeds up to 20 Gbps, with latency levels dropping to just a few milliseconds. These capabilities have already enabled new applications such as ultra-high-definition video streaming, real-time cloud gaming, and the initial wave of smart city infrastructure.
5G introduced three key performance categories:
5G networks operate primarily in the sub-6 GHz and millimeter-wave (mmWave) spectrum bands, which offer high bandwidth but come with range limitations. The technology’s architecture also integrates edge computing and network slicing to improve efficiency and customize services for specific industries.
Despite its strengths, 5G’s rollout has faced challenges such as:
These limitations are shaping the expectations and ambitions surrounding 6G, highlighting the 5G vs 6G technology differences.
While 5G is still expanding globally, research on 6G technology is already gaining traction. 6G is expected to operate in the terahertz (THz) frequency range between 95 GHz and 3 THz, offering ultra-wide bandwidths for high-speed data transfer and extremely low latency.
6G is also expected to deliver theoretical speeds up to 1 terabit per second (Tbps), around 50 times faster than 5G. However, such figures are still under experimental study and have not been validated in real-world deployments.
6G will move beyond traditional communication models. It is envisioned to:
This AI telecom evolution will redefine how humans and machines interact, fostering ultra-connected ecosystems that extend beyond connectivity into cognition and automation. This demonstrates how 6G is different from 5G in data transfer.
The leap from 5G to 6G represents both quantitative and qualitative advances in mobile network technology. While 5G laid the foundation for ultra-fast communication and low latency, 6G aims to elevate connectivity to new levels of intelligence, precision, and efficiency. The two generations differ fundamentally across several parameters, including speed, latency, frequency spectrum, architecture, and technological integration. This section highlights the 6G vs 5G network performance.
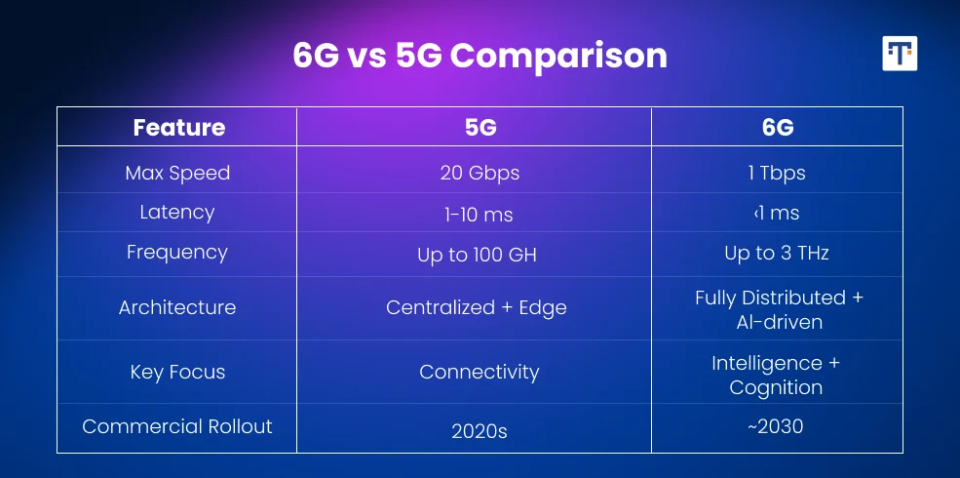
Latency, how long it takes data to travel between a source and destination, is another critical metric in the difference between 6G vs 5G network performance.
The frequency spectrum defines how much data a network can carry and over what distances. The progression from 5G to 6G brings a substantial shift in the operating spectrum bands.
The structural design of mobile networks is evolving from centralized control models to more dynamic, distributed frameworks.
The most profound difference between 5G and 6G lies in the integration of advanced technologies directly into the network core.
The commercial rollout of 6G is projected around 2030, following extensive research, standardization, and field trials. Organizations like 3GPP and the International Telecommunication Union (ITU) will lead efforts in defining technical standards and interoperability frameworks.
Key contributors in early research include:
Difference between 6G vs 5G is a fundamental reimagining of connectivity. As 5G continues to evolve globally, the future of 6G technology is paving the way for the next era of communication, one defined by instant responsiveness, immersive experiences, and deep integration of digital and physical systems.
Overcoming technical and regulatory hurdles will determine how quickly this vision becomes reality, but the trajectory is clear: mobile networks are set to become the central nervous system of future societies. The comparison of 6G vs 5G in IoT and smart devices highlights the 6G vs 5G impact on future communications, showcasing how 6G is different from 5G in data transfer at both individual and enterprise scales.

Sign up to receive our newsletter featuring the latest tech trends, in-depth articles, and exclusive insights. Stay ahead of the curve!